Important Reference
- https://www.mofa.go.jp/j_info/visit/visa/index.html
- https://visa.vfsglobal.com/ind/en/jpn/apply-visa
- Visa form
- https://www.mofa.go.jp/j_info/visit/visa/long/index.html
- https://www.mofa.go.jp/j_info/visit/visa/short/other_visa.html
Types of Visa Provided by Japan


Japan offers a variety of visa types to accommodate different purposes of visit. These visas are categorized mainly based on the length of stay, purpose of the visit, and the applicant’s qualifications. Here’s an overview of some of the primary types of visas provided by Japan:
1. Short-term Visa
- Tourist Visa: For sightseeing, visiting friends, or non-business-related activities.
- Business Visa: For short business trips, attending conferences, negotiations, or signing contracts.
- Transit Visa: For those transiting through Japan to another destination.
2. Long-term Visa
- Working Visas: For those who have specific skills or occupational qualifications. This category includes various visas, such as:
- Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services: For professionals in IT, engineering, legal, economic, and scientific fields, etc.
- Intra-company Transferee: For employees transferring to a branch in Japan.
- Skilled Labor: For people with particular skills, such as chefs or sports trainers.
- Business Manager: For those starting a business in Japan or managing a business.
- General Visas: These are typically for non-working purposes but allow longer stays than tourist visas, including:
- Cultural Activities: For participants in cultural activities or studies, including unpaid internships.
- Student Visa: For those enrolled in Japanese educational institutions.
- Trainee Visa: For individuals undergoing training in Japan.
- Dependent Visa: For the spouse and children of someone holding a work or student visa in Japan.
3. Specified Visas
- Specified Skilled Worker: For individuals with certain skills needed in specific industries, allowing them to work in Japan.
- Technical Intern Training: For people undergoing technical intern training in Japan in various fields.
4. Family-related Visas
- Spouse or Child of Japanese National: For the spouse or child of a Japanese national or permanent resident.
- Long Term Resident: For those who have permission to stay in Japan for a specific purpose that doesn’t fit other categories, including long-term residents with Japanese ancestry.
5. Diplomatic and Official Visas
- For those traveling to Japan on official or diplomatic business for their home country or international organization.
Permanent Residency
- While not a visa per se, permanent residency can be applied for by those who have lived in Japan for a certain period and meet specific criteria, allowing them to stay in Japan indefinitely.
Step by Step to apply Visa for Japan
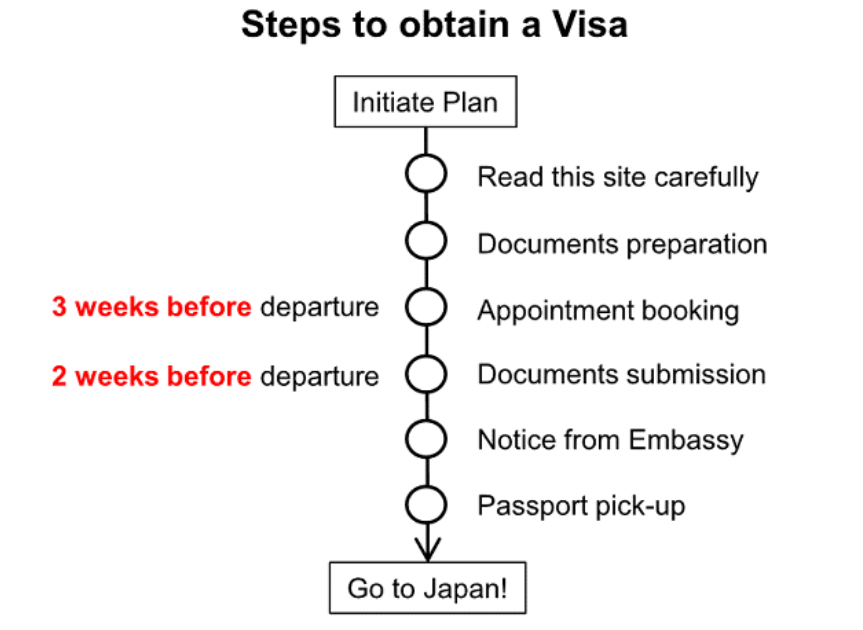
Step 1: Determine Your Visa Type
- Identify the type of visa you need based on your purpose of visit (e.g., tourism, business, work, study, family visit).
Step 2: Gather Required Documents
- Common requirements include a valid passport, a visa application form, passport-sized photos, and flight itinerary.
- For work or long-term visas, a Certificate of Eligibility (COE) issued by the Ministry of Justice in Japan is often required.
- Depending on the visa type, additional documents may be needed, such as financial statements, invitation letters, or proof of accommodation.
Step 3: Complete the Visa Application Form
- Download the visa application form from the website of the Embassy or Consulate of Japan in your country, or obtain a copy directly from their office.
- Fill out the form accurately. Incomplete or incorrect forms can result in application denial.
Step 4: Submit Your Application
- Depending on your location, submit your visa application along with all the required documents to the Japanese embassy or consulate, or the designated application center in your country, such as VFS Global in India.
- Some countries may allow you to submit your application via mail or through an accredited travel agency.
Step 5: Pay the Visa Fee
- Visa fees vary depending on the visa type and your nationality. Payment is usually required upon application submission. Note that visa fees are non-refundable, even if the visa is not granted or is cancelled.
Step 6: Attend the Interview (If Required)
- Some visa categories may require you to attend an interview at the embassy or consulate. You will be notified if an interview is necessary.
Step 7: Track Your Application
- After submission, you can track the status of your visa application through the embassy, consulate, or application center’s website, if available.
Step 8: Collect Your Visa
- Once processed, you will be notified about the decision. If granted, you will need to collect your passport with the visa from the embassy, consulate, or application center, or it may be sent to you by mail if this service is offered.
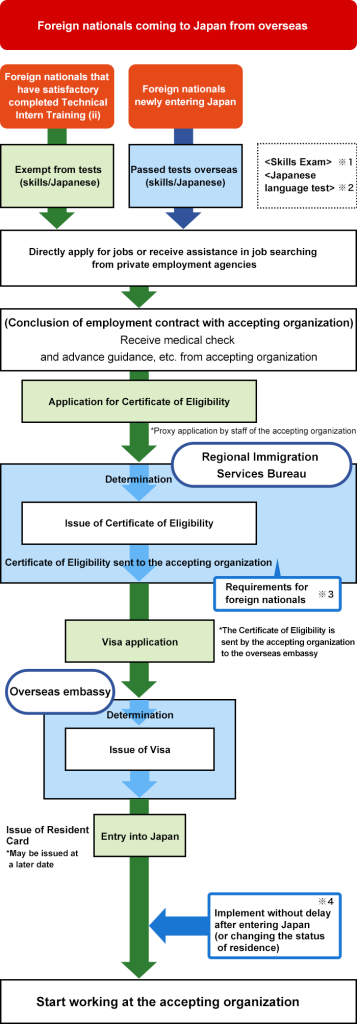
Procedures Chart for Work or Long-Term Stay
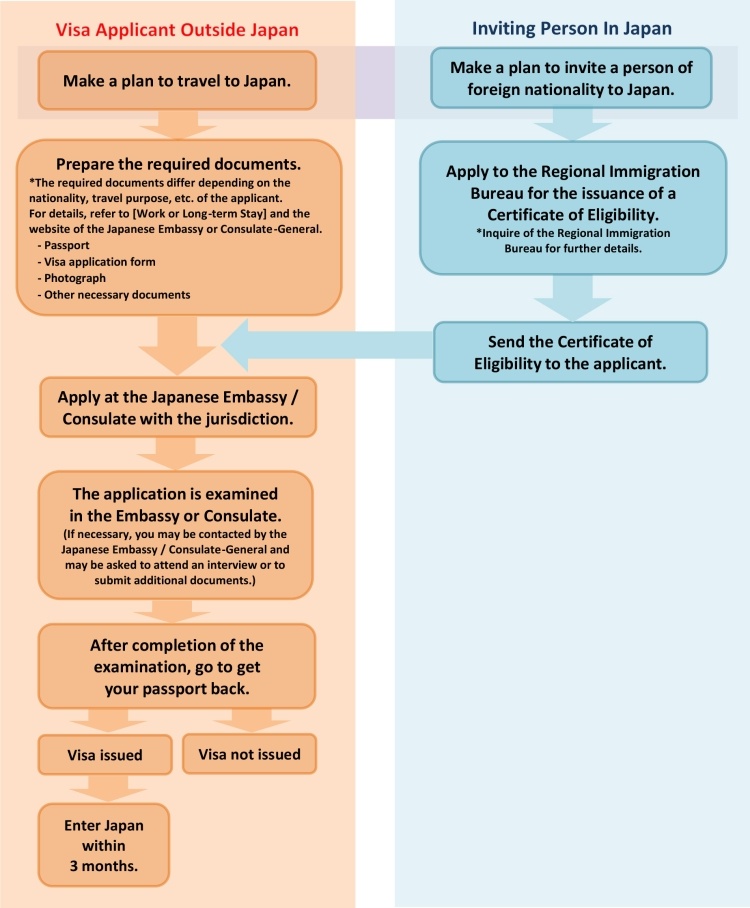
How to apply Visa for Japan from India?

Applying for a visa to Japan from India involves several steps, guided by the type of visa you are applying for (tourist, work, student, etc.). The process typically involves gathering required documentation, including a valid Certificate of Eligibility (COE) for certain visa types, submitting your application at a Japanese embassy or consulate, and possibly attending an interview. Here’s a general overview of how to apply for a Japanese visa from India:
Japan has partnered with VFS Global in India to streamline the visa application process for Indian citizens. VFS Global manages visa application centers for Japan in several cities across India, facilitating the submission of visa applications and the collection of biometrics. Here’s how to apply for a Japanese visa through VFS Global in India:
1. Determine the Type of Visa
First, determine the appropriate visa type based on your purpose of visit (e.g., tourism, work, study). Each visa type has specific requirements and allowed activities.
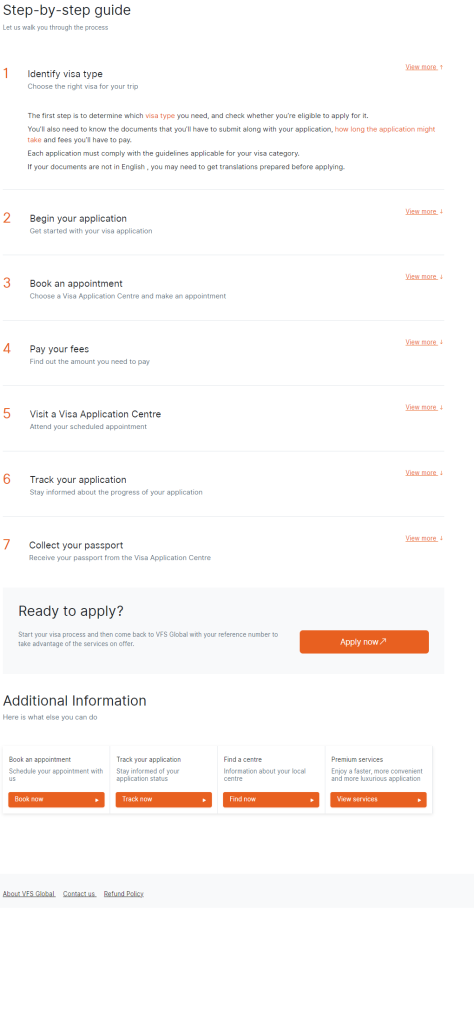
2. Gather Required Documents
Commonly required documents include:
- Passport: Valid for the duration of your stay with at least two blank pages.
- Visa Application Form: Completed and signed. The form is available on the website of the Embassy of Japan in India or at the consulate offices.
- Photograph: Passport-sized and taken within the past six months.
- Certificate of Eligibility (COE): Required for work, student, and some other long-term visas. This should be obtained by your sponsor in Japan and sent to you.
- Proof of Financial Means: Such as bank statements, to show you can support yourself during your stay.
- Flight Itinerary and Accommodation Details: For tourist visa applicants.
- Additional Documents: Depending on the visa type, additional documents related to your employment, educational institution, or host in Japan may be required.
3. Submit Your Application
Submit your visa application along with all the required documents to the Japanese embassy or consulate in India. There are Japanese consular services in several cities including New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Bengaluru. Some visa applications can be submitted through accredited travel agencies.
4. Pay the Visa Fee
Visa fees vary based on the type of visa and are subject to change. Fees are paid at the time of application submission or upon collection of the visa, depending on the consulate’s policy.
5. Attend an Interview (If Required)
For some visa types, you may be required to attend an interview at the embassy or consulate. You’ll be informed of this requirement when you submit your application.
6. Collect Your Visa
Once your application is processed, you will be notified about the decision. If approved, you will need to collect your passport with the visa or it may be sent to you, depending on the service options offered by the embassy or consulate.
Additional Tips
- Start Early: Begin the application process well in advance of your planned departure date. Processing times can vary.
- Check for Updates: Visa requirements and procedures can change. Always verify the current requirements on the official website of the Embassy of Japan in India or by contacting the consulate directly.
- Accurate Information: Ensure all information provided in your application is accurate and complete. Discrepancies or missing information can lead to delays or denial of your visa.
For the most accurate and updated information, refer to the Embassy of Japan in India website or contact the nearest Japanese consulate.
What is Certificate of Eligibility (COE)?
The Certificate of Eligibility (COE) is a crucial document in the process of obtaining a visa for Japan, especially for long-term visas such as those for work, study, family reunion, or residency. Issued by the Immigration Services Agency of Japan, the COE verifies that the applicant meets the requirements to enter Japan under a specific status of residence. Here’s a breakdown of what the COE entails and its significance:
Purpose
- Pre-screening: The COE serves as a pre-screening process by the Japanese immigration authorities to ensure that the applicant qualifies for a particular status of residence in Japan before arriving in the country.
- Streamlines Visa Application: With a COE, the visa application process at the Japanese embassy or consulate in your country becomes smoother and often faster, as the major evaluation regarding your eligibility has already been done by the immigration authorities in Japan.
Application Process
- Application by Proxy in Japan: The application for a COE is usually submitted in Japan by a sponsor on behalf of the applicant. The sponsor can be an employer, a school, a family member, or a legal representative, depending on the visa type.
- Required Documentation: The sponsor must provide detailed information about themselves and the applicant, including the purpose of the applicant’s stay, proof of financial support, and other relevant details.
- Processing Time: The processing time for a COE can vary from a few weeks to several months, depending on the visa category and the specifics of the application.
After Receiving the COE
- Apply for a Visa: Once you have received your COE, you must apply for a visa at a Japanese embassy or consulate in your home country. The COE must be submitted with your visa application.
- Validity: The COE is typically valid for three months from the date of issue, so it’s important to apply for your visa and enter Japan within this timeframe.
Benefits
- Evidence of Eligibility: The COE is concrete evidence that you meet the criteria for your desired status of residence in Japan.
- Facilitates Entry: Having a COE can facilitate a smoother entry process into Japan, as immigration officials will have already reviewed and approved your eligibility for the status of residence.
Importance
The COE is a critical step for anyone looking to reside in Japan for an extended period, whether for work, study, family reasons, or other long-term stays. It not only demonstrates eligibility and compliance with Japanese immigration laws but also significantly aids in the visa application and entry process.